ANSYS SOLDER JOINT RELIABILITY SIMULATION SOLUTIONS
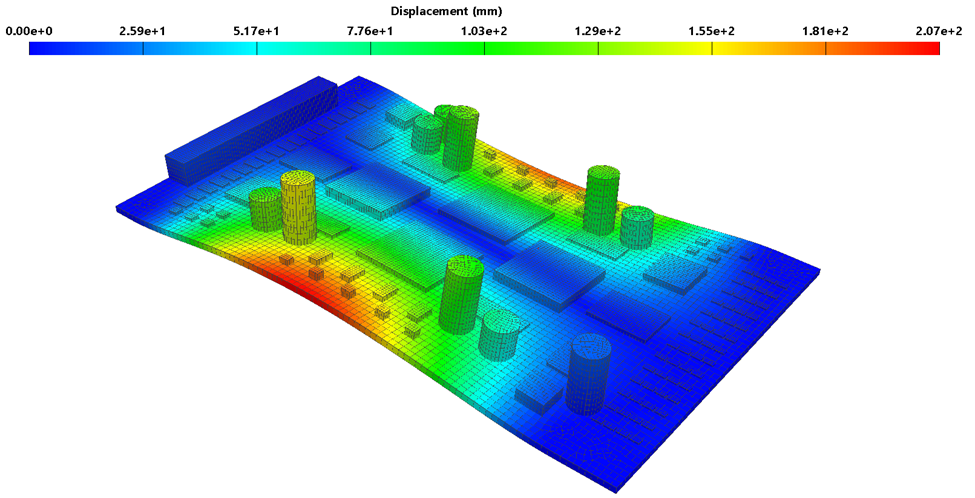
In today’s competitive business environment balancing the conflicting demands of miniaturization, performance and efficiency are paramount. In demanding Ball Grid Array (BGA) applications, the solder joints are a primary point of failure. With the advent of 2.5D packaging and beyond, the number of joints and bumps are under greater and newer stresses than ever. For maintaining a technology lead in today’s economic climate, simulation is more crucial than ever. The modern BGA design will need to evaluate cyclic fatigue, thermal stress/performance, drop test and even electromigration early on in the design process to keep up.
For predicting the operating cycles to fatigue, the effect of temperature cycling is evaluated. Nonlinear material properties of the solder joint are employed to evaluate the rate of non-elastic stress accumulation. The Darveaux model is used to overcome the problem of stress singularities in material interfaces. Using these procedures, the fatigue life of a design can be evaluated, relative to other designs.
The challenges of modeling the BGA arise from a number of conditions:
- The small length scale of the most vulnerable part (solder) relative to the rest of the component
- The higher & ever increasing # of solder bumps/joints
- The material interfaces & resulting stress singularities
- The nonlinear nature of the solder material (creep, plasticity, Anand’s commonly used)
- Because many of these effects are interdependent, predicting the reliability of solder joints in devices is a complex problem. ANSYS Multiphysics has emerged as the industry and academic standard for modeling these issues.
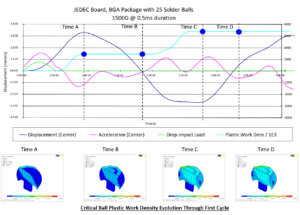
Critical ball plastic work density evolution through first cycle.
Electromigration is a difficult coupled physics problem involving structural, electric, thermal and diffusive terms. Ansys Multiphysics has had the capabilities to solve this challenging problem. In addition to developing a training course on this topic, Ozen Engineering also has streamlined the process with an ACT Extension.
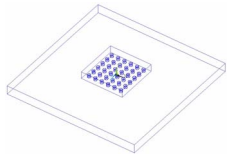
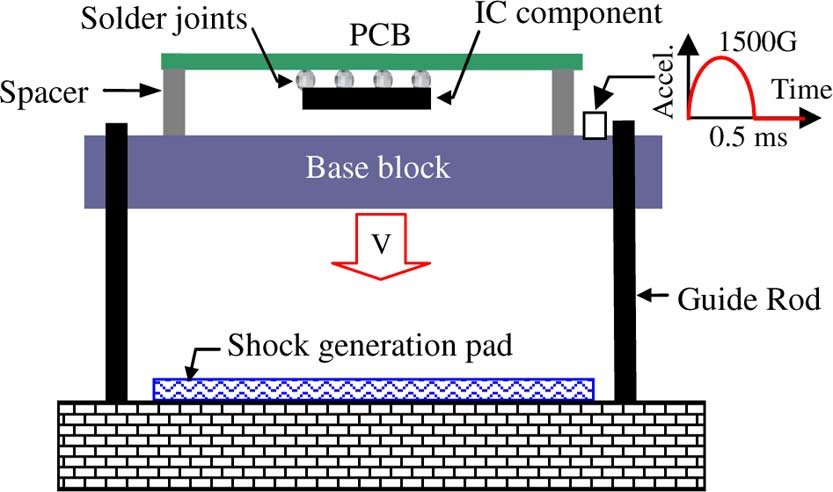
Drop tests are a JEDEC (JESD22-B111) requirement that can be evaluated in silico to save physical testing time and money. Here the overall assembly is modeled first and a detailed submodel of the solder joints is subsequently created and analyzed. This is one approach to the length scale challenges of the solder joints relative to the entire device, yielding a very efficient simulation.


![Ansys-elite-channel-partner-horizontal-reversed[1]](https://www.ozeninc.com/uploads/2022/06/Ansys-elite-channel-partner-horizontal-reversed1.png)